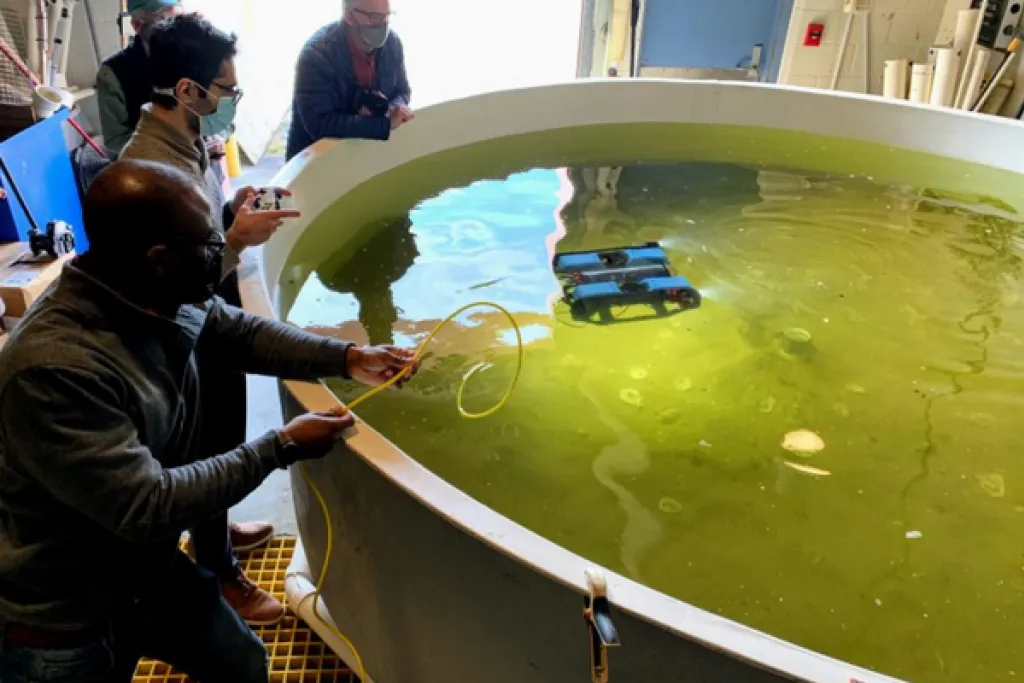
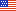
Shellfish aquaculture is perhaps the most sustainable form of aquaculture. Oysters filter water and provide habitat for many marine species. They contribute to national food security and provide numerous health benefits. Shellfish aquaculture is also an important economic driver for rural coastal areas, providing jobs and sustaining economic viability.
However, domestic shellfish aquaculture is bottlenecked by outdated technology and tools, preventing high-volume production. For example, on-bottom oyster farming methods have not substantially changed since the 19th century. Planting and harvesting methods are random and lack precision, leading to extremely low survival rate and production.
To address the sustainability issues of the current shellfish farming, University of Maryland scientists are developing smart precision farming practices with support from USDA’s National Institute of Food and Agriculture that will lead to sustainable shellfish production and improve farmers’ lives.
“The robotics and artificial intelligence technologies being developed would bring significant advances to shellfish farming industry, enhancing productivities and profitability,” said Miao Yu, associate professor of mechanical engineering at the University of Maryland. “Although the oyster farmers don’t fully understand the technology tools that we are developing, to our surprise, we received tremendous support on our project. The farmers are very interested in accessing the environmental and crop inventory monitoring data and using precision farming practices to improve farm management.”
Currently, scientists are developing underwater robotics-based monitoring and smart-harvesting technologies to enable precision shellfish farming. In the long term, researchers will go from precision shellfish farming to digital, programmable aquaculture that would help address food insecurity and mitigate climate change, ultimately addressing the grand challenge of global ecosystem sustainability.
Preliminary economic studies show that modest increase of 10% oyster production will result in an annual increase in revenues of more than $11 million for Maryland farmers and more than $228 million nationwide.
“This production increase will lead to the removal of over 65 tons of nitrogen fertilizers from sea water,” Yu said. “More production will lead to expanded sales and increased consumption. Research suggested that 10% replacement of beef consumption with oysters would result in greenhouse gas emission reduction equivalent of having 10.8 million fewer cars on the road. Ultimately, this project will lead us to a more sustainable future.”
Additional information about this research will be presented at a NIFA education session at Aquaculture America 2023 Feb. 23-26 in New Orleans. NIFA national program leader Dr. Tim Sullivan, who provides leadership for programs in aquaculture, animal health and biotechnology, will moderate a session highlighting the breadth and impact of NIFA-funded aquaculture research and outreach.
Top image: University of Maryland scientists are developing smart precision farming practices using robotics and artificial intelligence technologies that will lead to sustainable shellfish production and improve farmers life. Credit: University of Maryland.